Most resources in this post are from Lynda.com AWS Essential Training.
Design for Failures
- Virtual servers
- EC2
- Elastic IP: no instance specific/Acount level/Easily remapped from instance to instance ***
- Regions and availibility zones * Amazon machine image (AMI**): packaged environment and settings
- Template for root volume
- Launch permissions
- Block device mapping
Templates are available in three ways: AMIs, AWS Marketplace and Community AMIs. * Elastic load balancing (ELB**): balancing network traffic across multiple EC2 instances within multiple availability zones.
Characteristics:
- Supports HTTP, HTTPS, TCP traffic
- Support health checks
- Automatically scales based on demands placed on it
- Singe CNAME for DNS configuration
*** Cloud monitoring: CloudWatch (Normally use for FREE)
 ***
***
Elastic Block Storage (EBS)
EBS snapshot
- Stored incrementally
- Only billed for amount of data that changed
- Deleting only removes what is not needed by other snapshots.
Manage relational database service (RDS)
Implement Elasticity: Automate Infrastructure
Decouple Components
Optimize For Performance
Caching: AWS Elasticache
Purpose of usage: Eliminate the database bottlenecks and speed up delivery of application data.
Thus, it is designed for “HOT” (request frequently) data for better performance. Traditionally, the in-memory cache is not suitable for scalling,
since the cache on certain server won’t be available for newly added servers’ access. This is where Elasticache helps, shown:
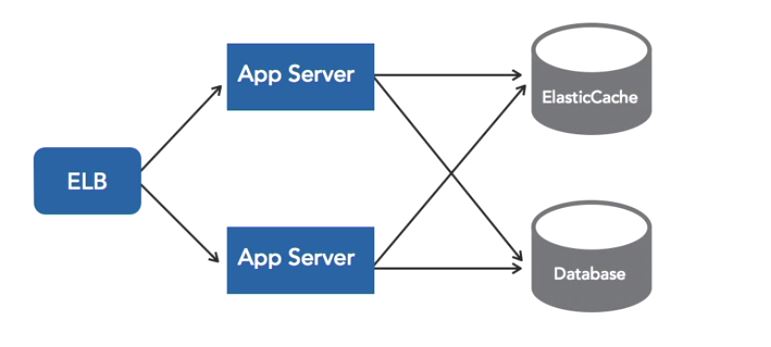
It supports 2 types of caches:
- Memcached
- Store strings
- Up to 1 MB value
- No persistence
- Easy to scale
- Redis
- Support string data
- Allows higher volume
- Support persistence
- Supports other data types, like lists, hashes, etc.
The way to choose which one depends on your use case (application). It is wiser to use Redis since it is easier to be expanded.
- Write-Through Pattern
- All data stored in memory -> Increased cache hit
- Require a lot of memory
- Lazy Load
- Only needed data are in cache -> Con of higher miss rate -> potential lower performance
So both ways can be used with the help of TTLs by keeping memory need minimized.
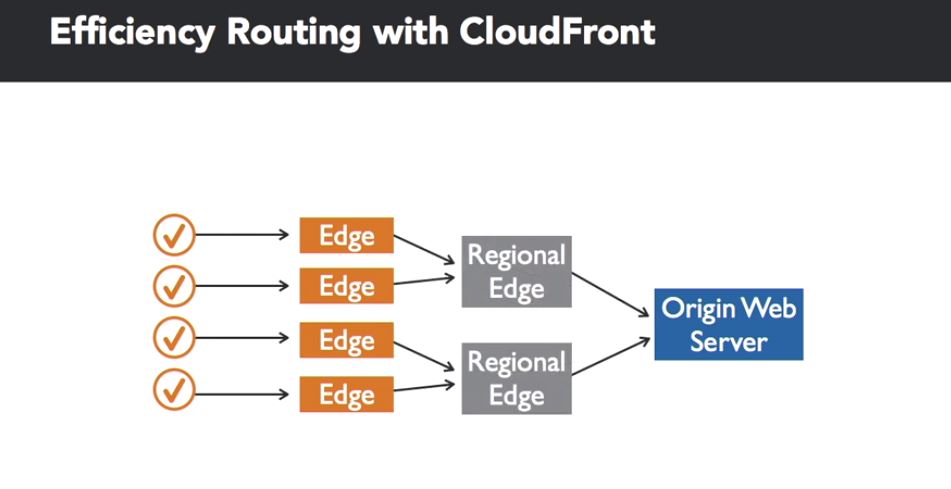
caching: AWS CloudFront
A CDN service keep the data in cache to speed up delivery of web and mobile application content. It also helps the scaling since it reduces the direct request to server.
Consists of:
- A distribution
- Edge locations
- Regional edge caches
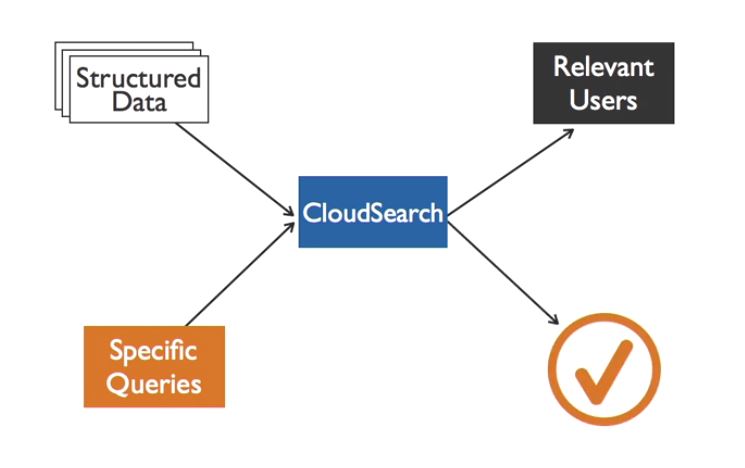
Search: AWS CloudSearch
A dedicated search engine to help improve user experience and maximize engagement.
Search Engines need to have features:
- fast
- reliable
- best results based on relevancy to the query
Serverless architectures: API gateway
Let the app uses the API gateway when API is required for an application.
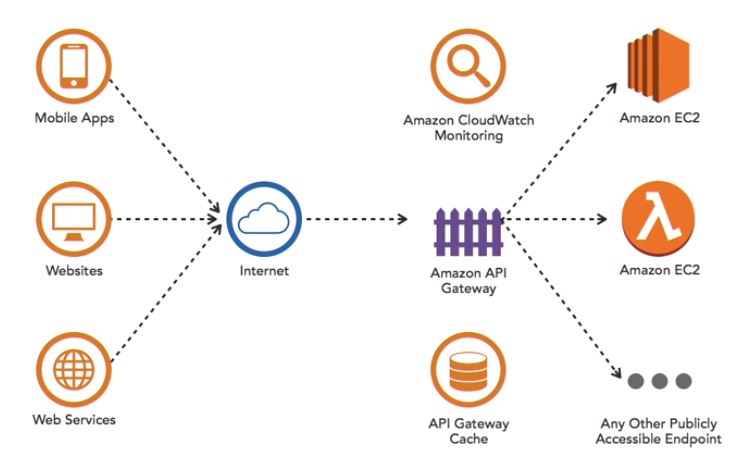
Additional features:
- Multiple versions and release stages
- Automatic SDK generation
- monitoring and logging
Serverless architectures: AWS Lambda
Two components:
- The lambda function itself (custom code uploaded to the server)
- Event source
- Other services of AWS
- Custom applications
Security
The shared security model
Shared security by both users and AWS together.
- Iaas(Infrastructure as a Service): The user takes more responsibilities
- Paas(Platform as a Service): AWS takes more responsibilities
- Saas(Software as a service): The user takes the least responsibilities
Identity and access management (IAM)
Keep resources secure.
Key points:
- Never use master account to access resources or manage services.
- Create separate users, groups, roles and permissions in IAM and only allow access when absolutely needed, and only to the specific resources that are needed.
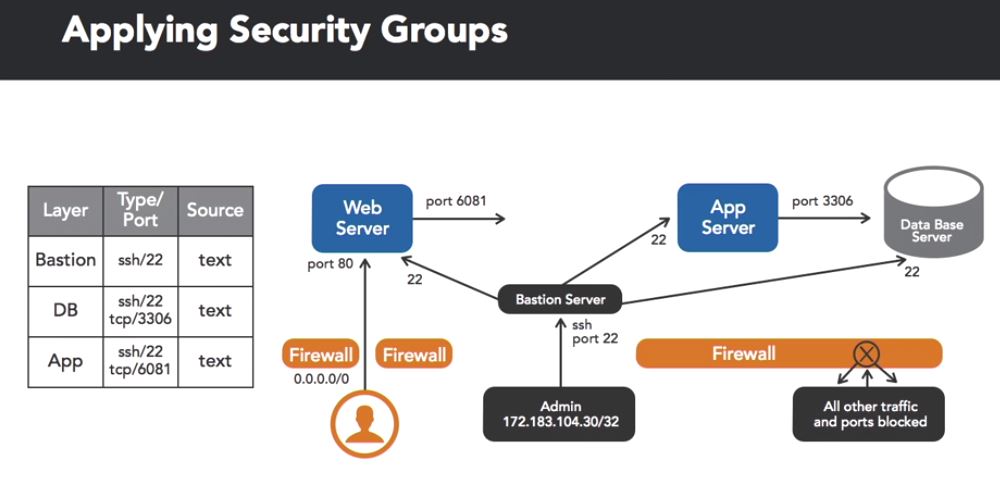
AWS Security Group
The virtual firewall of AWS. Rules are created to control the traffic via type (SSH, RDP, HTTPS) and Protocol (TCP, UDP), Port range, Source (IP address or security group).
This is an example:
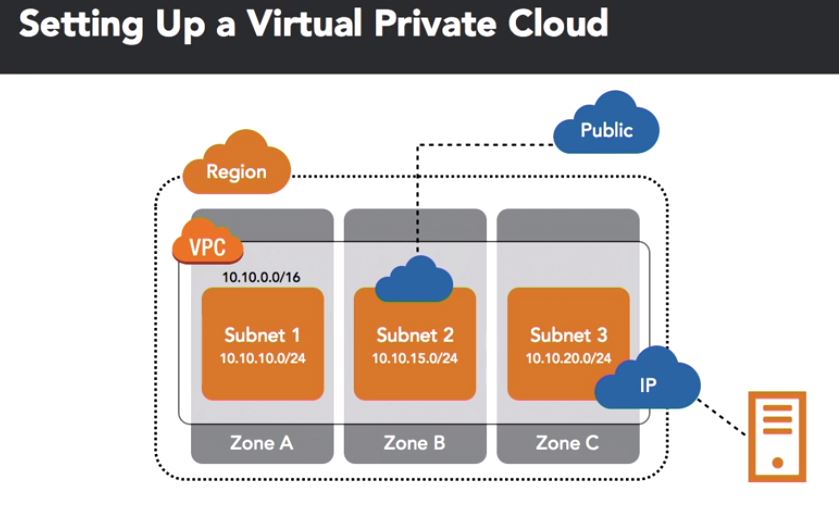
Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
Characteristics:
- Logically isolated to only one AWS account
- Not automatically addressable via the public internet
- Private and public interface control
- Both inbound and outbound traffic can be controlled
- Multiple IP addresses can be assigned
- Elastic interface networks can be assigned
- VPN connection
…
So it is complicated to configure a VPC. Good news is that AWS offers default VPC, with it:
- No configuration steps
- Ready to use
Example below:
optimize for Cost
AWS provides four instance purchasing options:
- On demand: hourly basis, no long-term commitment. Pay when running. ->
- Reserved: one-time but low payment, significant discount on hourly charge -> For committed utilization
- Spot: bid on the market for unused capacity based on the supply and demand -> For time insensitive workloads
- Dedicated hosting (Not clear yet)
Set Up a Web Application Architecture with Servers
An example setting up a web server:
- S3: setting up the web hosting
- Lambda and the gateway API to manipulate data
- DynamoDB: storing data which can be used by the web application