Description
Given n non-negative integers a1, a2, …, an , where each represents a point at coordinate (i, ai). n vertical lines are drawn such that the two endpoints of line i is at (i, ai) and (i, 0). Find two lines, which together with x-axis forms a container, such that the container contains the most water.
Note: You may not slant the container and n is at least 2.
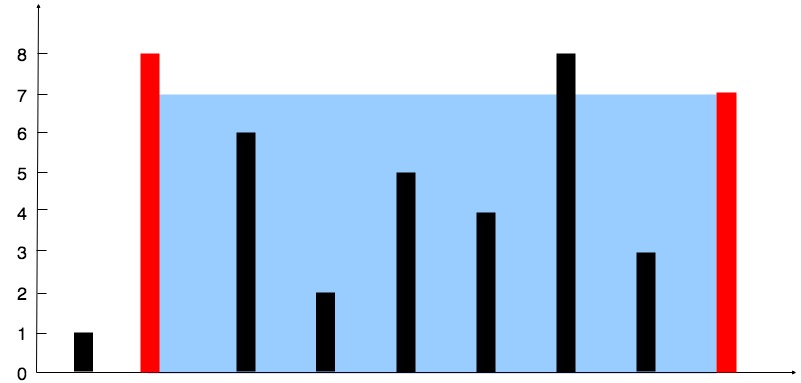
The above vertical lines are represented by array [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]. In this case, the max area of water (blue section) the container can contain is 49.
Example:
1
2
Input: [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]
Output: 49
Approach 1
Iteration 1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
class Solution:
def maxArea(self, height: List[int]) -> int:
area = 0
for i in range(len(height)):
for j in range(len(height)):
area = max(area, (j-i)*min(height[i], height[j]))
return area
Result: ❌
Above codes has time complexity of O(nˆ2), work for short list, but failed for test case with 5000 elements, caused Time limit exceeded error.
Iteration 2
In order to make it less time complex, we need to think about things below:
- Possible to just loop the array once, namely in O(n) time?
- Subsequently, how to make sure max area can be found without calculating area between every pair of lines in brute force way in iteration 1?
Let’s review the area calculation logic again:
min(left_height, right_height) * (right_index - left_index)
So the area is always limited by the smaller height among two, and distance between two lines (width), which means, in order to increase the area, the lower height bound needs to be increased while distance between lines should be maximized.
An idea is to take two pointers, one from leftmost and the other one from the rightmost of the array, then moving pointers inwards, and for each step, only keep the higher line from both sides as the this is the potential way to increase the area, but calculate the area with the lower line, plus also because with moving pointer inwards, the width getting smaller, the area can only get smaller with the same height.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
class Solution:
def maxArea(self, height: List[int]) -> int:
area = 0
n = len(height)
i, j = 0, n - 1
while i < j:
if height[i] < height[j]:
area = max(area, (j-i)*height[i])
i +=1
else:
area = max(area, (j-i)*height[j])
j -=1
return area
Result: ✅
Runtime: 124 ms, faster than 88.07% of Python3 online submissions for Container With Most Water.
Memory Usage: 15.5 MB, less than 5.26% of Python3 online submissions for Container With Most Water.
Time complexity O(n) and space complexity O(1).